The Rise of Natural Gas Vehicles in the US Automotive Market

Introduction
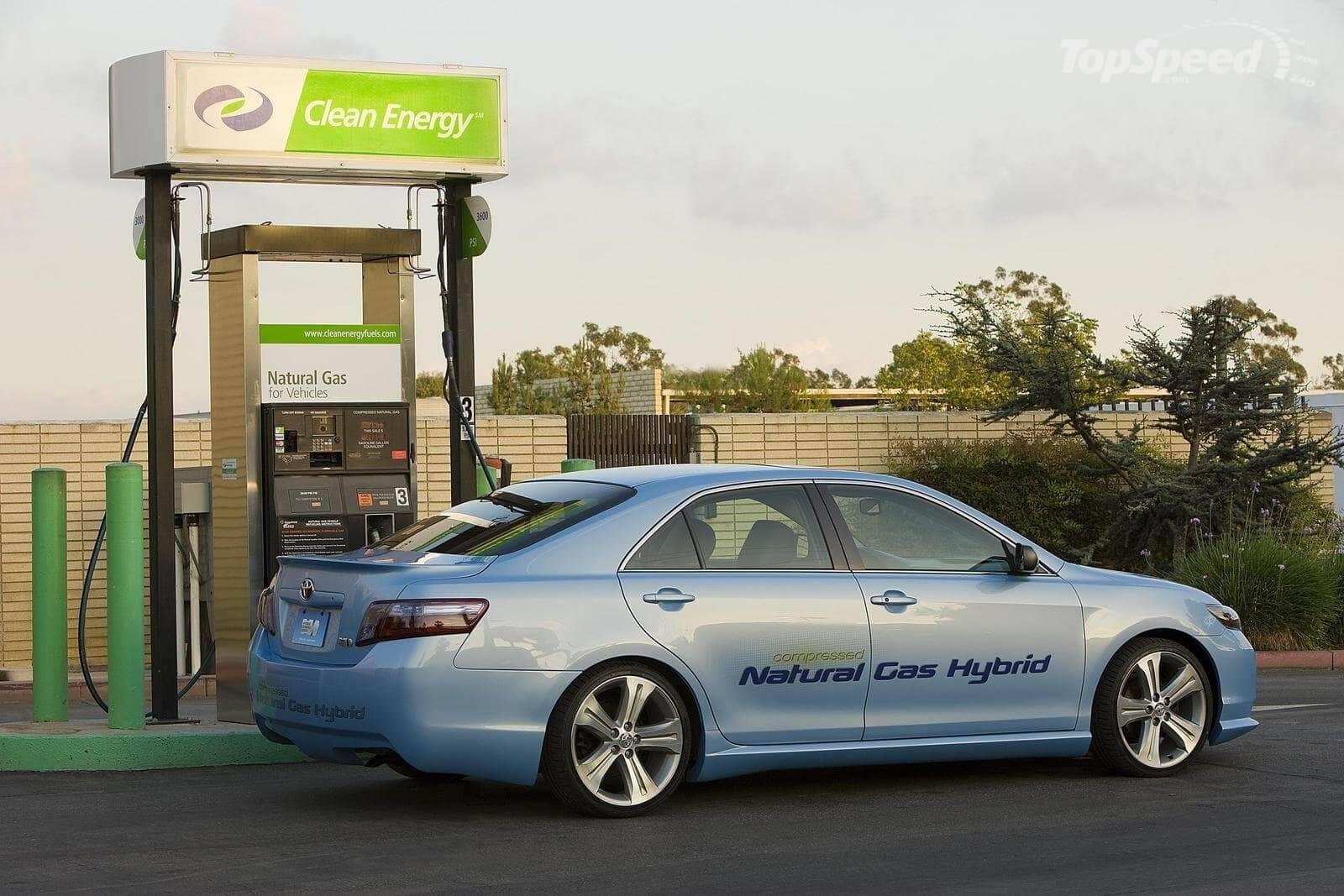
The US Automotive Natural Gas Vehicle (NGV) Market is gaining momentum as the nation transitions toward cleaner and more sustainable transportation solutions. With growing concerns about air pollution, carbon emissions, and energy security, natural gas has emerged as an efficient alternative fuel for both commercial and passenger vehicles. Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) vehicles offer significant advantages over conventional gasoline and diesel engines, including lower emissions, reduced fuel costs, and quieter operation. Supported by government initiatives, tax incentives, and infrastructure development, the adoption of natural gas vehicles is expanding across logistics fleets, public transport systems, and corporate operations. The market is set to play a critical role in the United States’ broader strategy for energy diversification and emission reduction.
Market Drivers
The increasing emphasis on reducing greenhouse gas emissions is a primary driver of the US NGV market. Natural gas vehicles emit up to 25% less CO₂ than gasoline-powered vehicles, making them a key component of the nation’s sustainable transport agenda. Rising fuel prices have made natural gas a cost-effective alternative, particularly for high-mileage fleets such as buses, trucks, and delivery vans. Federal and state-level incentives, including grants for fleet conversion and fueling infrastructure development, are accelerating adoption. Additionally, advancements in CNG and LNG engine technology are enhancing vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and durability. Major logistics and transportation companies are transitioning their fleets to natural gas to meet sustainability targets and reduce operational costs, further boosting market growth.
Market Challenges
Despite strong potential, the NGV market faces challenges related to infrastructure, cost, and awareness. Limited availability of refueling stations remains a significant barrier, especially in rural and remote areas. The high upfront cost of NGV systems and conversion kits can deter individual consumers and small fleet operators. Moreover, public perception and lack of understanding regarding the safety and performance of natural gas vehicles hinder wider adoption. Competition from electric vehicles (EVs), which receive substantial government support and rapid technological advancements, also limits NGV growth. Maintenance complexities and the need for specialized servicing infrastructure add further operational challenges, requiring industry-wide collaboration to address.
Market Opportunities
The US NGV market presents multiple opportunities as the demand for clean energy vehicles accelerates. Expansion of public and private CNG/LNG fueling networks is a major opportunity, particularly along long-haul transport routes and urban corridors. Technological innovations in biogas and renewable natural gas (RNG) production are opening new possibilities for carbon-neutral transportation. Fleet operators in sectors such as logistics, waste management, and municipal services are key potential adopters due to predictable routes and high fuel consumption. Additionally, partnerships between automakers and energy companies are facilitating the rollout of next-generation natural gas engines with improved efficiency and lower emissions. Government-led green fleet programs and public transportation modernization initiatives will further boost market adoption.
Regional Insights
Regionally, California, Texas, and New York are leading states in NGV adoption due to supportive policies and advanced fueling infrastructure. California’s stringent emission regulations and incentives for alternative fuels make it a national leader in natural gas mobility. Texas, with its strong energy industry and logistics networks, has witnessed rapid deployment of CNG trucks and buses. The Midwest region is increasingly investing in biogas projects, converting agricultural and landfill waste into renewable natural gas for vehicle use. The East Coast, supported by urban transport modernization programs, is adopting CNG-powered public buses and corporate fleets. Overall, growing infrastructure investment and collaboration between state governments and energy companies are fueling regional market expansion.
Future Outlook
The future of the US NGV market is promising as the nation seeks balanced pathways toward low-carbon mobility. Over the next decade, a combination of renewable natural gas adoption, engine innovation, and infrastructure expansion will make natural gas vehicles more accessible and sustainable. Integration of hybrid CNG-electric systems could enhance performance while further reducing emissions. The rise of smart refueling networks and digital fleet management systems will improve efficiency and cost tracking for commercial users. As renewable energy and biogas technologies mature, the carbon footprint of NGVs will continue to decrease. While electric mobility may dominate in passenger segments, natural gas will remain a strategic alternative for heavy-duty and long-haul transport, ensuring energy diversification and resilience in the US automotive landscape.
Conclusion
The US Automotive Natural Gas Vehicle Market is evolving as a key contributor to sustainable and cost-efficient transportation. Backed by policy support, corporate fleet adoption, and renewable energy integration, natural gas vehicles are reshaping how America moves goods and people. Though challenges such as infrastructure and cost persist, ongoing technological progress and public-private collaboration are paving the way for greater adoption. As the US continues its transition toward cleaner mobility, NGVs will serve as an important bridge technology—delivering immediate environmental and economic benefits while complementing the long-term growth of electric and hydrogen vehicles.