Airborne Wind Turbine Market Explained

Introduction
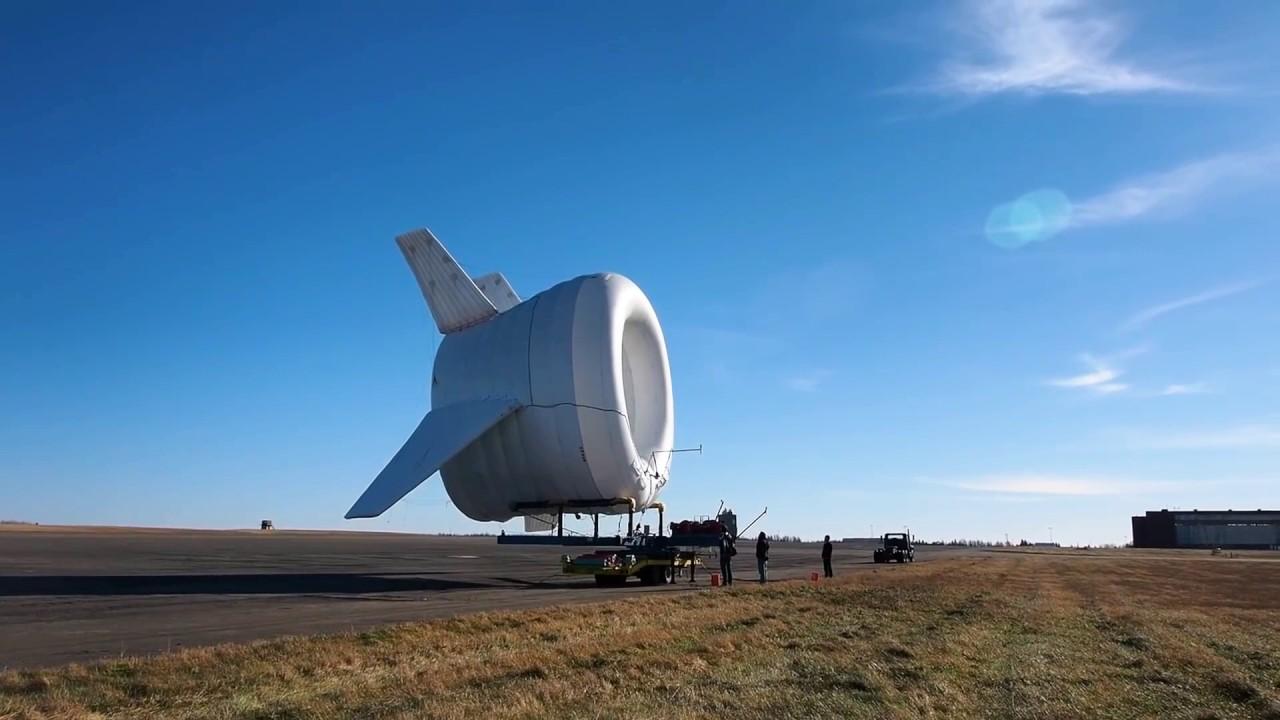
The airborne wind turbine market represents an innovative frontier in renewable energy, aiming to harness stronger and more consistent winds found at higher altitudes compared to conventional ground based turbines. Airborne wind energy systems generate electricity using tethered flying devices such as kites, drones, or aerostats that capture wind energy hundreds of meters above ground. These systems transmit power to the ground through tethers or onboard generation units. By accessing high altitude winds, airborne wind turbines promise higher capacity factors, reduced material usage, and deployment flexibility. The technology has attracted interest as countries seek cost effective, low carbon energy solutions with minimal land use. Although still in developmental and early commercialization stages, airborne wind turbines are gaining attention as a complementary solution within the broader renewable energy mix.
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the airborne wind turbine market is the global push toward renewable and low carbon energy generation. High altitude winds are typically stronger and more consistent than surface winds, offering the potential for increased energy yield. Limited land availability and environmental concerns associated with large wind farms encourage exploration of alternatives with smaller physical footprints. Airborne systems require less steel, concrete, and infrastructure compared to conventional turbines, potentially reducing capital costs and environmental impact. Growing demand for off grid and remote power solutions supports interest in portable and rapidly deployable airborne wind systems. Government funding for clean energy research and pilot projects further accelerates technological development. Additionally, advancements in materials, autonomous control systems, and power electronics support the feasibility of airborne wind energy.
Market Challenges
Despite its promise, the airborne wind turbine market faces significant challenges. Technical complexity related to flight control, stability, and power transmission remains a major hurdle. Ensuring safety and reliability in varying weather conditions is critical, particularly for operations near populated areas or aviation routes. Regulatory frameworks for airspace use and energy generation are still evolving, creating uncertainty for commercialization. Durability of tethers and airborne components under continuous mechanical stress affects system lifespan. Grid integration and power quality management present additional challenges. High research and development costs and limited commercial scale deployments slow market maturity. Overcoming these challenges requires continued testing, regulatory collaboration, and technological refinement.
Market Opportunities
The airborne wind turbine market offers notable opportunities driven by innovation and niche applications. Remote and island communities lacking grid access can benefit from airborne wind systems that are easier to transport and install than traditional turbines. Military, disaster relief, and temporary power applications represent early use cases due to rapid deployment capability. Hybrid energy systems combining airborne wind with solar and storage enhance reliability and energy output. Advances in autonomous operation and artificial intelligence improve flight optimization and reduce operational costs. Growing interest in floating offshore renewable solutions creates opportunities for airborne wind systems deployed at sea. As technology matures, economies of scale and standardization can unlock broader commercial adoption.
Regional Insights
Europe is a leading region in airborne wind turbine development due to strong renewable energy policies and active research programs. Several pilot projects and startups are based in this region, supported by government and institutional funding. North America shows growing interest driven by clean energy innovation and defense related applications. Asia Pacific presents long term potential due to rising energy demand and interest in decentralized renewable solutions. The Middle East and Africa may explore airborne wind to support off grid power generation and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Regional growth is influenced by research investment, regulatory openness, and renewable energy targets rather than immediate large scale deployment.
Future Outlook
The future of the airborne wind turbine market will depend on successful transition from pilot projects to commercial scale systems. Continued improvements in materials, control algorithms, and power conversion efficiency are expected to enhance reliability and reduce costs. Regulatory clarity regarding airspace usage will be critical for wider adoption. While airborne wind is unlikely to replace conventional wind energy, it can complement existing technologies by accessing untapped wind resources. Long term growth will be supported by demand for innovative, low impact renewable energy solutions. As climate goals intensify, airborne wind turbines may become an important niche contributor to diversified renewable portfolios.
Conclusion
The airborne wind turbine market represents a bold and innovative approach to renewable energy generation by tapping high altitude wind resources. Strong drivers such as sustainability goals, land use constraints, and technological advancement support market interest. Although challenges related to technical complexity, safety, and regulation remain, ongoing research and pilot deployments are addressing these barriers. Opportunities in remote power, hybrid systems, and offshore applications enhance long term potential. As renewable energy systems evolve, airborne wind turbines may play a valuable role in expanding clean energy capacity and resilience worldwide.