Power Converter Market Explained

Introduction
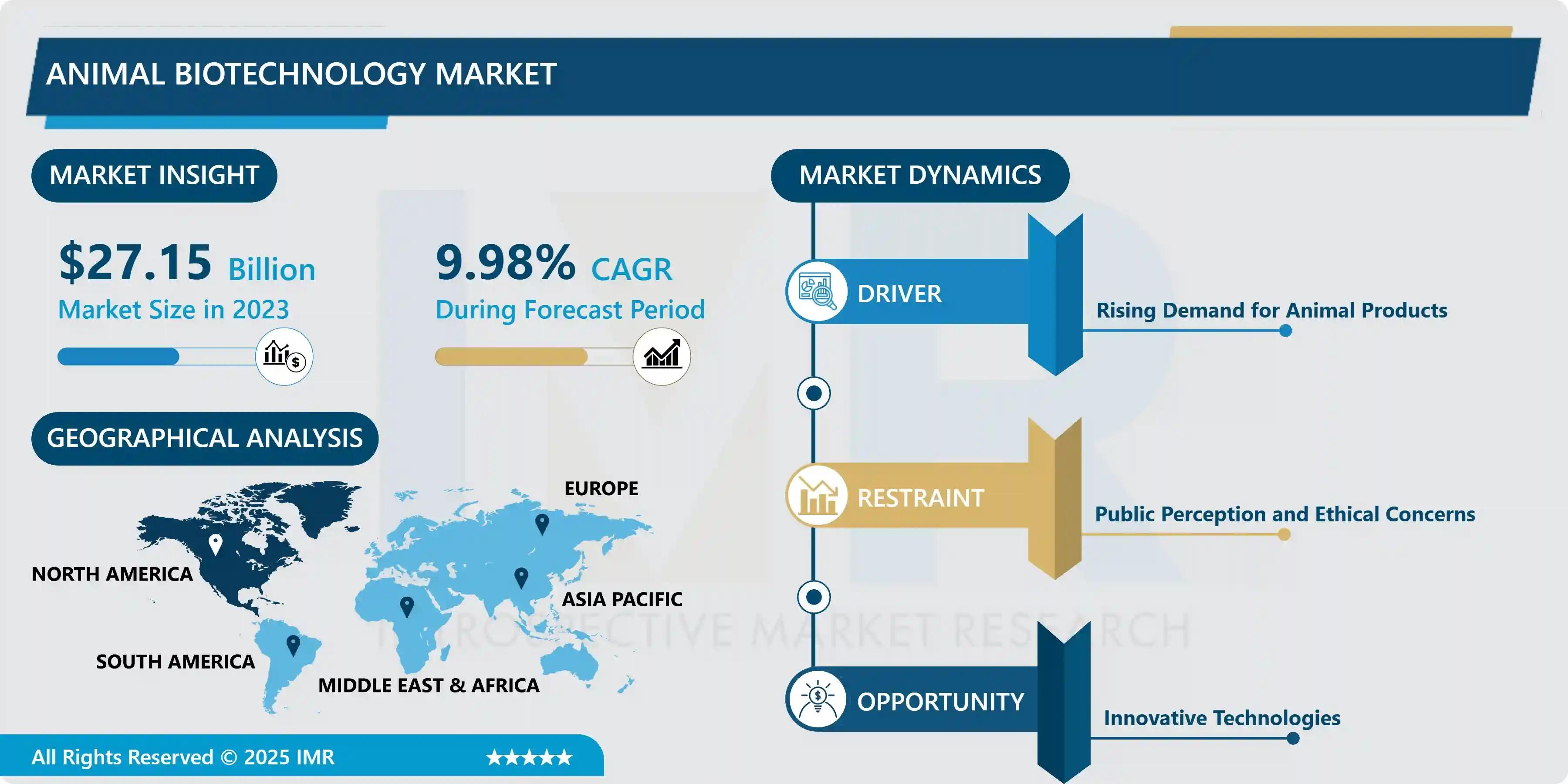
The power converter market is a fundamental segment of the global power electronics industry, enabling efficient conversion, control, and management of electrical energy across a wide range of applications. Power converters transform electrical power from one form to another, such as alternating current to direct current, direct current to alternating current, or changing voltage and frequency levels to meet specific system requirements. These devices are essential in renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, industrial automation, consumer electronics, data centers, telecommunications, and power transmission infrastructure. As electrification expands and energy efficiency becomes a strategic priority, demand for advanced power conversion solutions continues to rise. Technological progress in semiconductors and digital control has significantly improved converter efficiency, reliability, and power density. With global energy systems becoming more complex and decentralized, the power converter market plays a critical role in ensuring stable, efficient, and flexible power delivery.
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the power converter market is the rapid growth of renewable energy generation. Solar photovoltaic and wind power systems rely heavily on power converters to integrate variable renewable output with electrical grids and end use equipment. Expansion of electric vehicles and charging infrastructure also drives strong demand for high efficiency converters in onboard chargers, powertrains, and fast charging stations. Industrial automation and smart manufacturing increase the need for precise power control in motor drives and process equipment. Rising deployment of data centers and telecommunications infrastructure supports demand for reliable and energy efficient power conversion solutions. Additionally, growing emphasis on energy efficiency standards and emission reduction encourages adoption of advanced converters with lower losses. Urbanization, digitalization, and electrification trends collectively reinforce sustained market growth.
Market Challenges
Despite robust demand, the power converter market faces several challenges. High development and manufacturing costs associated with advanced semiconductor materials and complex designs can limit affordability. Thermal management and reliability issues become more pronounced as power density increases, requiring sophisticated cooling solutions. Rapid technological evolution shortens product life cycles and increases research and development pressure on manufacturers. Integration of power converters into diverse systems requires compatibility with varying standards and grid codes, adding complexity. Supply chain disruptions and semiconductor shortages can affect production timelines and pricing. Additionally, intense competition among manufacturers puts pressure on margins. Addressing these challenges requires continuous innovation, supply chain resilience, and cost optimization strategies.
Market Opportunities
The power converter market offers significant opportunities driven by emerging technologies and applications. Adoption of wide bandgap semiconductors such as silicon carbide and gallium nitride enables higher efficiency, higher switching frequencies, and compact designs. Growth of energy storage systems increases demand for bidirectional converters that manage charging and discharging cycles. Electrification of transportation, including railways and aviation support systems, expands application scope. Smart grids and microgrids create opportunities for converters with advanced control, communication, and grid support functions. Expansion of renewable energy in emerging markets offers long term growth potential. Modular and scalable converter architectures enable flexible deployment across multiple applications. These opportunities position power converters as critical enablers of next generation energy systems.
Regional Insights
Asia Pacific dominates the power converter market due to strong manufacturing capacity, rapid industrialization, and large scale deployment of renewable energy and electronics. Countries in this region are major producers and consumers of power electronic components. North America represents a significant market driven by electric vehicle adoption, data center expansion, and grid modernization initiatives. Europe shows steady growth supported by renewable energy targets, electrification policies, and advanced industrial automation. The Middle East and Africa are emerging markets where power infrastructure development and renewable projects drive demand. Latin America also demonstrates growing adoption as energy access and industrial activity increase. Regional market dynamics reflect differences in industrial growth, energy policy, and technology adoption.
Future Outlook
The future of the power converter market appears highly promising as electrification and digital energy management accelerate globally. Continued innovation in semiconductor materials and packaging will improve efficiency, reduce size, and enhance thermal performance. Integration of artificial intelligence and digital control will enable adaptive and self optimizing power conversion systems. Demand from electric mobility, renewable energy, and smart infrastructure is expected to remain strong. Regulatory emphasis on energy efficiency will further drive adoption of advanced converters. While competition and technology complexity will remain, manufacturers that invest in innovation and application specific solutions are likely to gain advantage. Long term growth will be supported by global energy transition and increasing reliance on electronic power control.
Conclusion
The power converter market is a cornerstone of modern electrical and electronic systems, enabling efficient energy conversion across diverse applications. Strong drivers such as renewable energy growth, electric mobility expansion, and industrial automation continue to fuel market demand. Although challenges related to cost, thermal management, and supply chains persist, technological advancements are addressing these issues. Opportunities in wide bandgap semiconductors, energy storage, and smart grids further enhance long term prospects. As energy systems evolve toward efficiency and flexibility, power converters will remain essential components supporting sustainable and reliable power delivery worldwide.