The Growing Importance of Rare Earth Metal Recycling
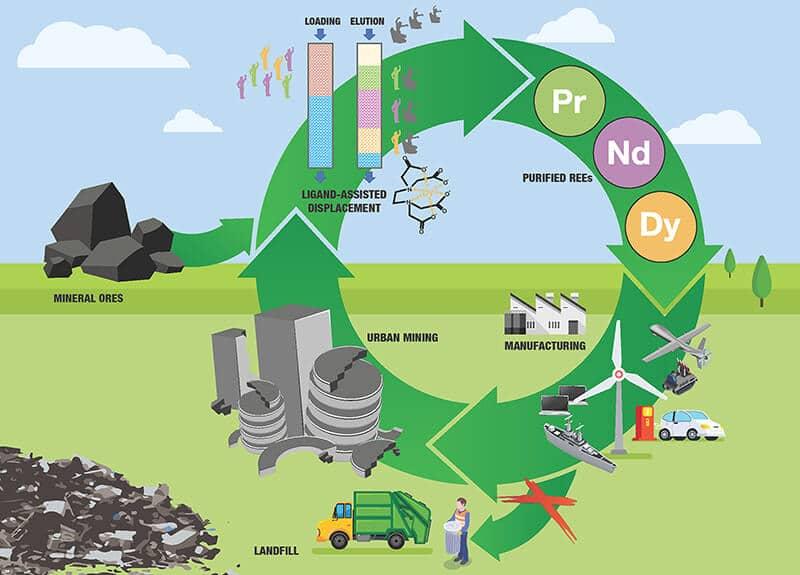
Introduction
The Rare Earth Metal Recycling Market is becoming increasingly vital as global demand for rare earth elements (REEs) rises across high-tech industries, renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, and advanced electronics. These metals—such as neodymium, dysprosium, terbium, yttrium, and lanthanum—are essential for manufacturing permanent magnets, batteries, semiconductors, and defense technologies. However, primary mining operations are limited to a few regions, generating supply chain vulnerabilities, geopolitical risks, and environmental concerns. Recycling rare earth metals offers a sustainable alternative by recovering valuable materials from end-of-life electronics, magnets, catalysts, and industrial waste. The growing emphasis on circular economy principles, resource security, and reduced environmental impact is fueling strong momentum in the global Rare Earth Metal Recycling Market.
Market Drivers
One of the major drivers is the skyrocketing demand for rare earth elements in clean energy technologies such as wind turbines, EV motors, fuel cells, and energy-efficient electronics. Supply chain concentration in countries like China has intensified global efforts to secure independent and sustainable rare earth sources. Environmental regulations also encourage recycling to reduce hazardous waste from electronic devices and industrial byproducts. Technological advancements in hydrometallurgical and pyrometallurgical recycling processes improve recovery efficiency and make recycling economically viable. Corporate sustainability initiatives and government-backed circular economy policies further accelerate market adoption.
Market Challenges
The Rare Earth Metal Recycling Market faces several obstacles despite its rising importance. Recycling processes are often complex, costly, and technically demanding due to the difficulty of extracting pure rare earths from mixed waste streams. Lack of standardized collection systems for end-of-life products results in inconsistent availability of recyclable materials. Many regions lack advanced recycling infrastructure, slowing market expansion. Additionally, fluctuating rare earth prices impact profitability, discouraging investment from new market entrants. Limited consumer awareness about recycling rare earth-containing products further contributes to low collection rates globally.
Market Opportunities
Significant opportunities are emerging in developing advanced recycling technologies that enhance extraction efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and improve cost-effectiveness. The growing volume of electronic waste worldwide presents a massive resource base for rare earth recovery. Increased EV adoption is creating new recycling pathways for motors and batteries containing rare earth magnets. Governments and global industries are investing in strategic recycling facilities to strengthen supply chain independence. Innovations in solvent extraction, bioleaching, and robotic dismantling systems open doors for scalable, automated recycling solutions. Partnerships between manufacturers, waste management companies, and technology providers bring additional opportunities for high-value recovery.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific leads the Rare Earth Metal Recycling Market due to strong recycling operations in China, Japan, and South Korea. These countries have well-established electronic manufacturing ecosystems and high volumes of end-of-life electronic products. Europe follows with significant investments in sustainable recycling infrastructure, driven by strict environmental regulations and circular economy policies. North America is expanding capacity through new recycling facilities aimed at reducing dependency on imported rare earths. Emerging regions in Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East show increasing interest as governments explore opportunities to reduce waste and participate in high-value global supply chains.
Future Outlook
The future of the Rare Earth Metal Recycling Market is strongly positive, driven by the rapid growth of electric mobility, renewable energy, and advanced digital technologies. Recycling will play a central role in diversifying supply sources and reducing environmental impact associated with rare earth extraction. With continuous advancements in extraction techniques, automated waste sorting, and high-efficiency recycling systems, costs are expected to decline steadily. Government policies supporting recycling-based manufacturing, green technology expansion, and strategic resource independence will further accelerate market development. More companies will adopt closed-loop production models, ensuring long-term sustainability and stable supply of rare earth elements.
Conclusion
Rare earth metal recycling is becoming a strategic necessity for global industries seeking secure, sustainable, and cost-efficient supply of critical materials. As technological innovations advance and governments intensify their focus on circular economy frameworks, recycling offers an effective pathway to reduce environmental impact and mitigate supply chain risks. Despite challenges related to cost, collection systems, and technical complexities, long-term market opportunities remain substantial. With strong demand from EVs, renewable energy systems, and electronics, the Rare Earth Metal Recycling Market is positioned for robust growth in the coming decade.




