Why Microinverters Are Powering the Future of Rooftop Solar

Introduction
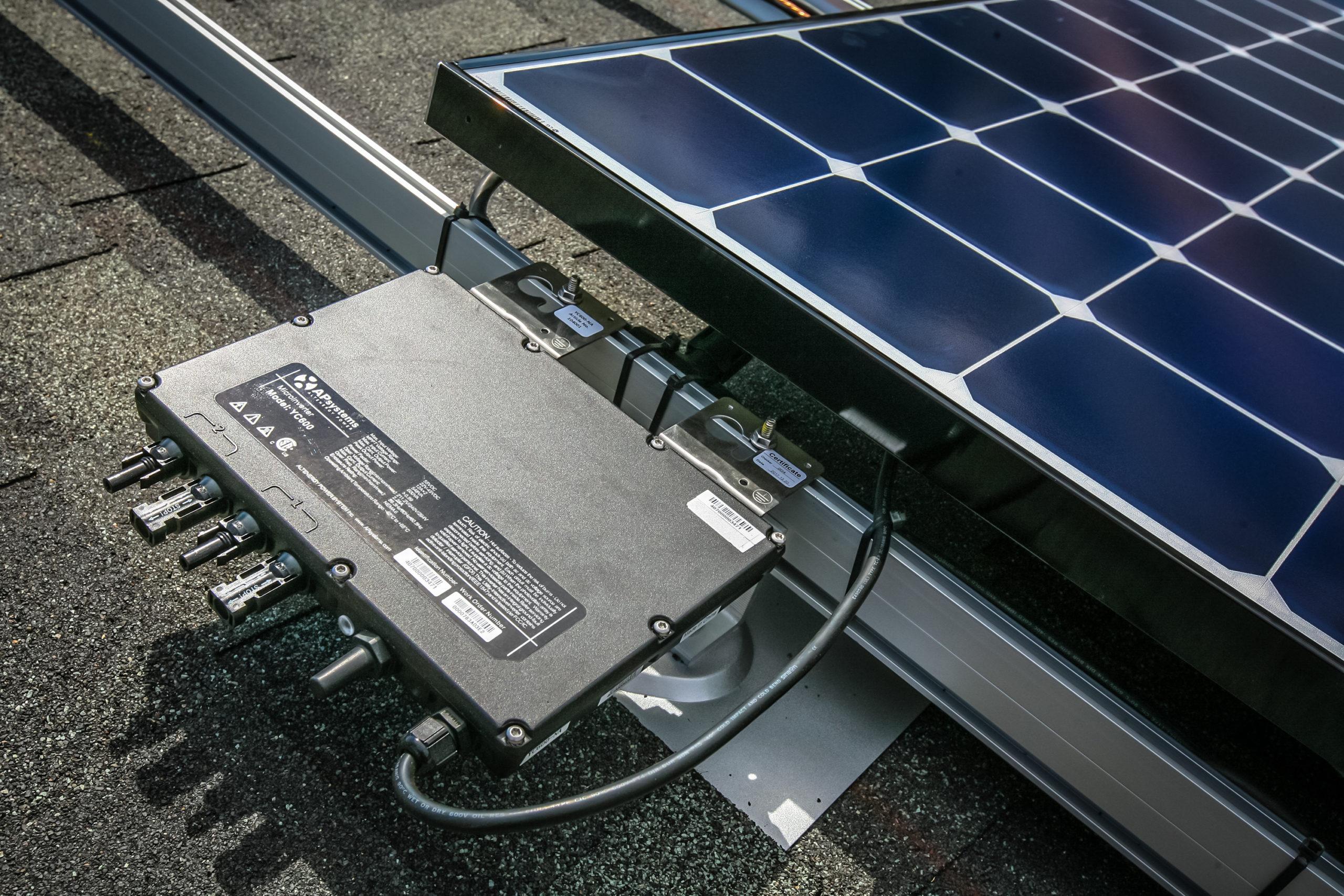
The Solar Microinverter Market is growing rapidly as residential and small commercial solar installations increasingly prioritize safety, efficiency, and module-level optimization. Microinverters convert DC electricity from each solar panel into AC at the module level, enabling maximum power output even when individual panels face shading, dirt, or orientation differences. Their ability to eliminate the single-point failure risk associated with string inverters makes them highly attractive for modern rooftop solar systems. With rising global energy costs, increased adoption of distributed solar, and stricter safety regulations, microinverters have become one of the most important technologies in the solar PV industry.
Market Drivers
A major driver of this market is the increasing preference for rooftop solar installations, particularly in residential spaces, where shading and complex roof layouts make microinverters ideal. Their module-level MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) capability maximizes output from each panel, significantly improving overall system efficiency. Safety regulations, especially rapid shutdown requirements in the United States and parts of Europe, are accelerating microinverter adoption. The growing use of high-wattage PV modules and bifacial panels also fuels demand for higher-capacity microinverters. Growth in off-grid and hybrid solar systems further boosts market expansion as microinverters offer greater flexibility and monitoring capabilities for distributed setups.
Market Challenges
Despite strong momentum, the Solar Microinverter Market faces challenges such as higher upfront costs compared to string inverters, making them less attractive for large commercial or utility-scale projects. Their installation on each module increases labor time and may require more complex maintenance. Microinverters are exposed to harsh rooftop temperatures, which can impact lifespan if the cooling design is not efficient. Compatibility issues can arise between certain microinverters and specific high-power PV modules. In regions where cost sensitivity is high, traditional string inverters continue to dominate. Additionally, limited technical awareness in emerging markets can slow microinverter adoption.
Market Opportunities
There are major opportunities in developing next-generation microinverters with higher watt capacity, advanced thermal management, and integrated communication systems. Growth in smart homes and distributed energy resources opens opportunities for microinverters that seamlessly connect with home batteries, EV chargers, and smart meters. Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Africa, and Latin America provide significant potential as rooftop solar adoption accelerates. Hybrid microinverters that support both solar generation and energy storage integration present strong prospects. Manufacturers offering long warranties, improved cooling designs, and IoT-based monitoring platforms will gain competitive advantages. Installers and EPC companies can expand their service offerings by including microinverter-based system packages.
Regional Insights
North America leads the Solar Microinverter Market due to strict safety regulations, high residential solar adoption, and strong presence of leading MLPE manufacturers. Europe demonstrates steady growth supported by sustainability initiatives, increasing rooftop solar installations, and rising electricity prices in countries such as Germany, Italy, Spain, and the Netherlands. Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with high adoption in Australia, Japan, South Korea, India, and China driven by distributed solar expansion. Latin America is witnessing rising demand in Brazil, Chile, and Mexico. The Middle East shows increasing interest in microinverter-based systems for residential and commercial rooftops, while Africa presents long-term opportunities in off-grid and hybrid solutions.
Future Outlook
The future of the Solar Microinverter Market will be shaped by advancements in semiconductor technologies, AI-driven monitoring, and integration with smart energy ecosystems. Microinverters will evolve to support higher wattage panels exceeding 500W and multi-module configurations for improved cost efficiency. Enhanced cooling systems, including passive and hybrid cooling designs, will extend product lifespan. Integration with energy management platforms will enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and grid-support functionalities. As battery storage becomes more affordable, microinverters optimized for solar-plus-storage systems will experience high demand. Continued cost reductions driven by scale and innovation will accelerate global adoption.
Conclusion
The Solar Microinverter Market continues to grow as homeowners and small businesses adopt advanced rooftop solar systems requiring high efficiency, safety, and module-level performance. Despite challenges involving cost, maintenance, and environmental exposure, strong demand arises from rapid solar expansion, evolving safety regulations, and smart energy adoption. Innovations in cooling, monitoring, and multi-module designs will shape future market growth. As distributed solar becomes a cornerstone of modern power systems, microinverters will remain essential for unlocking maximum PV performance and long-term reliability.