Understanding Growth Trends in the Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market

Introduction
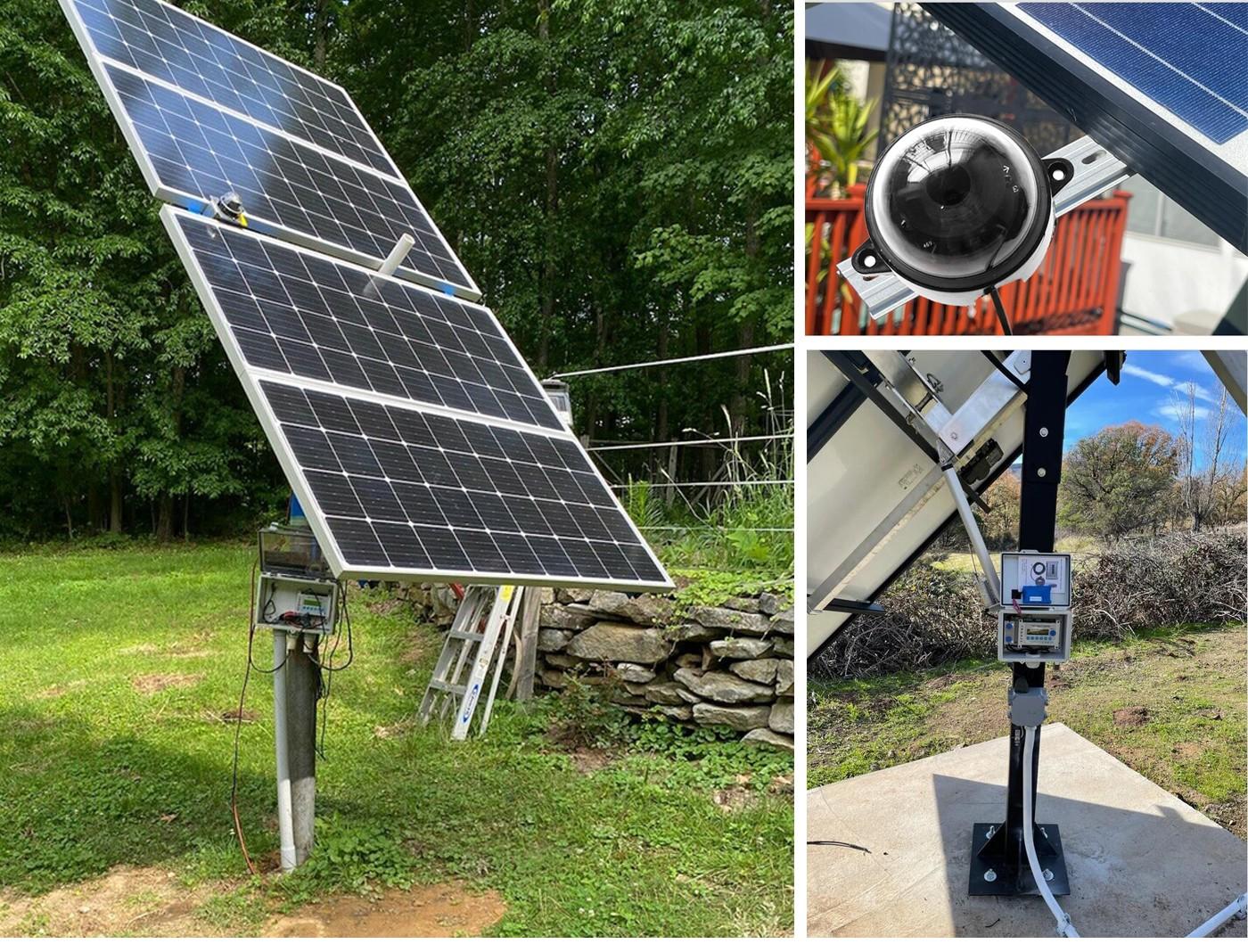
The Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market is gaining significant momentum as solar power developers seek technologies that maximize energy generation efficiency. Single axis solar photovoltaic trackers are mechanical systems that rotate solar panels along one axis, typically from east to west, allowing panels to follow the sun’s movement throughout the day. This tracking capability enables higher energy yield compared to fixed-tilt solar installations, making single axis trackers a preferred solution for large-scale solar projects. As global demand for clean and cost-effective energy increases, solar developers are increasingly adopting tracking systems to improve project economics. With declining solar component costs and rising utility-scale solar installations, the single axis solar PV tracker market is emerging as a key enabler of optimized solar power generation worldwide.
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers of the Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market is the growing demand for utility-scale solar power projects. Large solar farms prioritize technologies that improve energy output without significantly increasing land or equipment costs, and single axis trackers offer an effective balance between performance and affordability. Another major driver is the continuous reduction in solar project levelized cost of electricity, where tracking systems play a crucial role by increasing annual energy yield. Government policies promoting renewable energy adoption and carbon reduction targets further accelerate market growth by encouraging large-scale solar installations. Technological advancements in tracker design, such as improved motors, control systems, and structural materials, have enhanced reliability and reduced maintenance needs. Additionally, increased investor confidence in solar infrastructure projects supports wider deployment of tracking systems.
Market Challenges
Despite strong growth prospects, the Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market faces several challenges. Higher initial installation costs compared to fixed-tilt systems can be a barrier, particularly for smaller projects with limited budgets. Mechanical complexity introduces risks related to wear, component failure, and maintenance requirements, especially in harsh environmental conditions such as high winds, sandstorms, or extreme temperatures. Land topography constraints can also limit tracker deployment, as uneven terrain may increase installation complexity and cost. Furthermore, grid interconnection delays and regulatory uncertainties in certain regions may slow solar project development, indirectly affecting tracker demand. Concerns related to long-term reliability and operational performance also require manufacturers to continuously invest in product testing and quality assurance.
Market Opportunities
The market presents substantial opportunities driven by innovation and expanding solar deployment. Advancements in control algorithms and smart tracking software are improving system accuracy, fault detection, and real-time performance optimization. Integration of single axis trackers with bifacial solar panels creates additional opportunity by enabling higher energy capture from both direct and reflected sunlight. Emerging markets with high solar irradiance and expanding power demand offer significant growth potential for tracker installations. Additionally, hybrid renewable energy projects combining solar with energy storage or wind power are increasing demand for efficient solar tracking solutions. As financing options improve and solar infrastructure investment grows, single axis trackers are expected to gain broader adoption across commercial and utility-scale projects.
Regional Insights
Regionally, North America holds a significant share of the Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market due to widespread adoption in large-scale solar farms and favorable renewable energy policies. Developers in this region increasingly prefer single axis trackers to maximize project returns. Asia-Pacific is expected to witness the fastest growth, driven by rapid solar capacity expansion, rising electricity demand, and government initiatives supporting renewable energy development. Countries with high solar potential are investing heavily in tracking technologies to optimize land use and energy output. Europe shows steady growth, supported by ambitious climate targets and increasing utility-scale solar projects. Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa are emerging regions where high solar irradiance and declining solar costs are encouraging tracker adoption.
Future Outlook
The future outlook for the Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market remains highly positive as solar energy continues to expand globally. Technological innovation is expected to further reduce system costs while improving durability and performance. Manufacturers are focusing on lightweight designs, corrosion-resistant materials, and advanced monitoring systems to enhance reliability. As solar power becomes a dominant source of new electricity capacity, the role of tracking systems in improving efficiency will become increasingly important. Policy support for renewable energy, coupled with corporate commitments to sustainability, will continue to drive demand. Over the long term, single axis trackers are likely to become a standard component of utility-scale solar projects.
Conclusion
The Single Axis Solar PV Tracker Market is a vital segment of the global solar energy industry, enabling higher energy output and improved project economics. Driven by the expansion of utility-scale solar installations, supportive government policies, and technological advancements, the market continues to grow across regions. While challenges related to cost, mechanical complexity, and environmental conditions persist, ongoing innovation is addressing these limitations. With increasing emphasis on renewable energy efficiency and large-scale solar deployment, single axis solar PV trackers are poised to play a crucial role in the future of sustainable power generation.