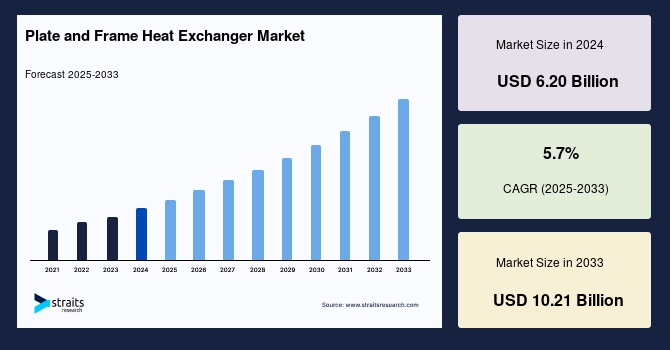
Graphite Electrode Market Dynamics: From Needle Coke to Furnace Efficiency
Steel is one of the most essential industrial materials in the world, supporting infrastructure, construction, transportation, energy, and manufacturing. As economies modernize and urbanize, steel demand remains strong. At the same time, the steel industry is undergoing a major shift toward cleaner production methods, and this transition is directly strengthening the graphite electrode business. Graphite electrodes are critical consumables in electric arc furnaces (EAFs), where they conduct electricity to generate intense heat for melting scrap steel and other metal inputs.
According to Market Research Future, the Graphite Electrode Market is experiencing significant growth as electric arc furnace steelmaking expands globally. Unlike traditional blast furnaces, EAF technology enables steel recycling and supports lower carbon emissions, which aligns with sustainability goals and environmental regulations. This shift is creating long-term demand for high-quality graphite electrodes across major steel-producing regions.
A key driver of the market is the rapid increase in scrap-based steel production. Many countries are investing in scrap collection and recycling systems, enabling a stronger supply of raw materials for EAF operations. Since graphite electrodes are consumed during furnace operation, electrode demand rises directly with EAF production volume. This makes the market closely linked to steel output trends and recycling growth.
Graphite electrodes are produced primarily from needle coke, a specialized petroleum-based raw material. The availability and pricing of needle coke can influence production costs, which impacts electrode pricing. In recent years, fluctuations in needle coke supply have created volatility in the electrode market. Manufacturers that can secure stable raw material supply chains gain a competitive advantage, especially during periods of high steel demand.
Another factor supporting growth is the increasing adoption of ultra-high power (UHP) electrodes. UHP electrodes are designed for high-performance EAF steelmaking, enabling faster melting and higher productivity. As steelmakers focus on efficiency, energy savings, and output improvement, demand for UHP electrodes is rising. This trend strengthens market value because premium electrodes command higher prices and require advanced manufacturing capabilities.
Regional growth patterns reflect industrial and infrastructure development. Asia-Pacific is a major market due to strong steel production, rapid urbanization, and growing EAF adoption. Europe is also expanding its EAF footprint as it pushes for greener steelmaking. North America remains a key market because of its established scrap recycling industry and strong EAF penetration.
In addition to steelmaking, graphite electrodes are used in other industrial applications such as ferroalloy production, silicon metal production, and certain chemical processes. These industries also require high-temperature electric furnaces, creating additional demand streams. However, steel remains the dominant application and continues to shape overall market direction.
A major indicator shaping future growth is Graphite Electrode Demand, which is expected to increase as global steelmakers accelerate their transition to cleaner, scrap-based production. This demand is also supported by government policies encouraging recycling, reducing emissions, and improving industrial energy efficiency.
Despite positive growth, the market faces challenges. Graphite electrode manufacturing is energy-intensive and requires specialized equipment, long production cycles, and strict quality control. Any disruption in production capacity can create supply shortages, which may lead to price spikes. Additionally, steel market downturns can reduce electrode consumption, making the industry sensitive to economic cycles.
Innovation continues to play a key role. Manufacturers are investing in improved electrode formulations, enhanced oxidation resistance, and better mechanical strength. These improvements help electrodes last longer and perform more efficiently in high-temperature furnace environments. Steelmakers benefit from reduced downtime and improved furnace productivity, which increases the attractiveness of premium electrode products.
In conclusion, the graphite electrode market is strongly positioned for growth due to the global shift toward electric arc furnace steelmaking, rising scrap recycling, and demand for high-performance UHP electrodes. With steel remaining a foundational industry worldwide, graphite electrodes will continue to be an essential consumable supporting modern steel production.